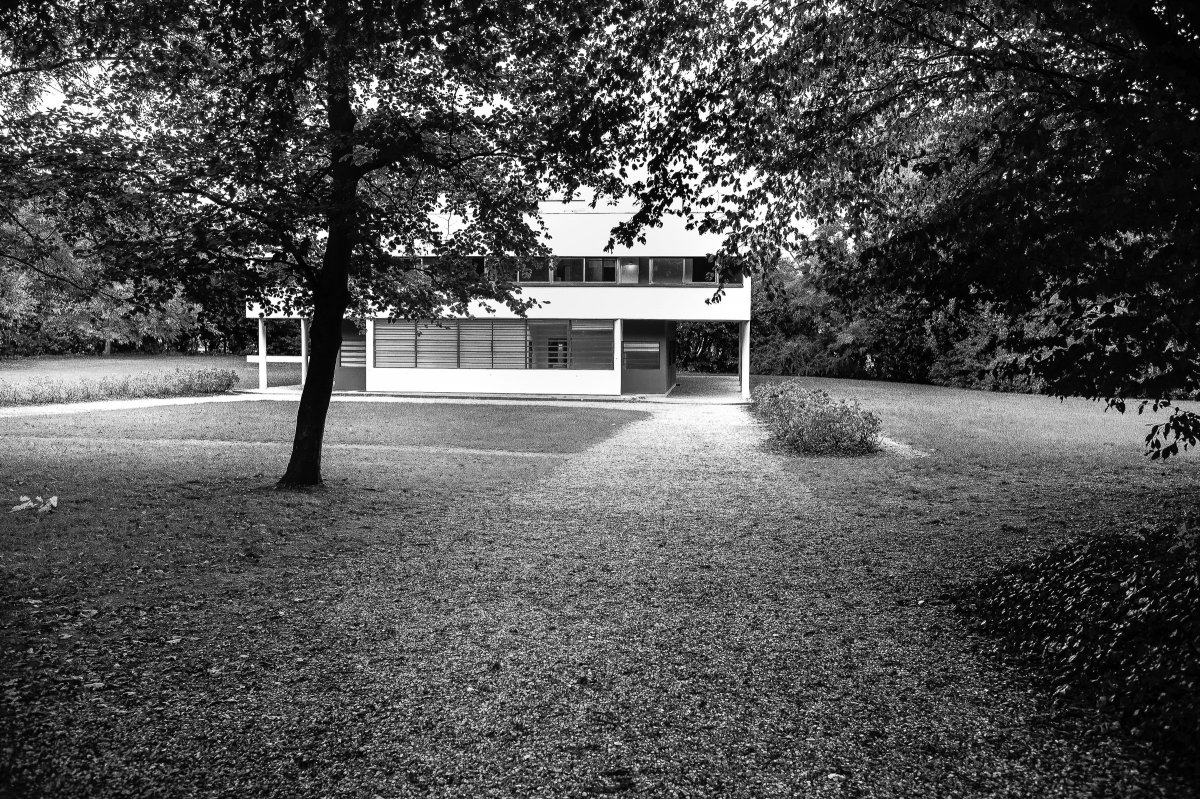
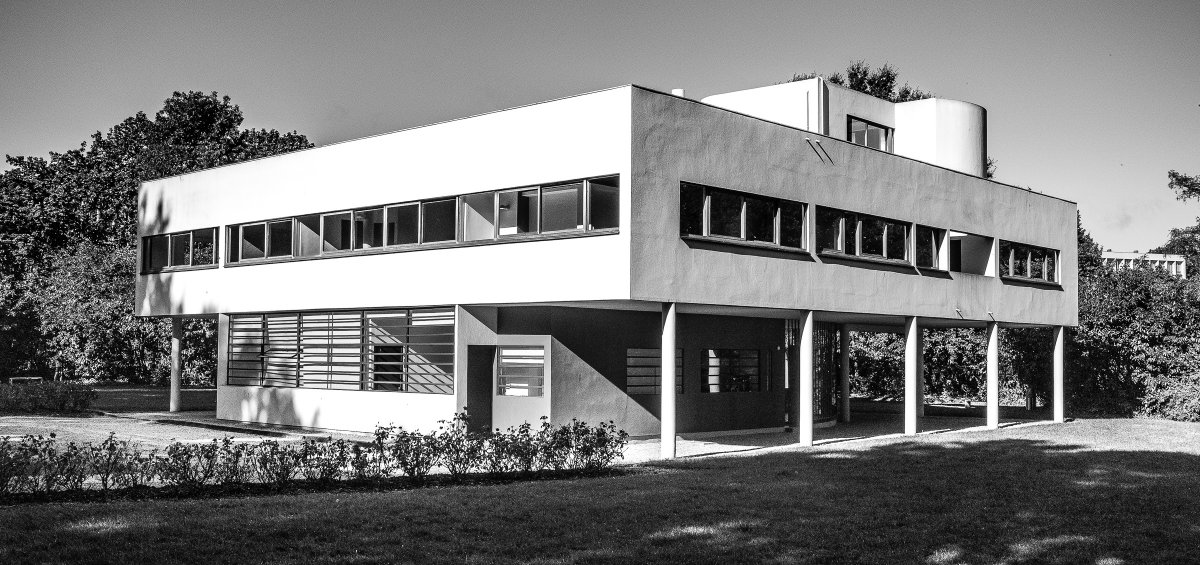
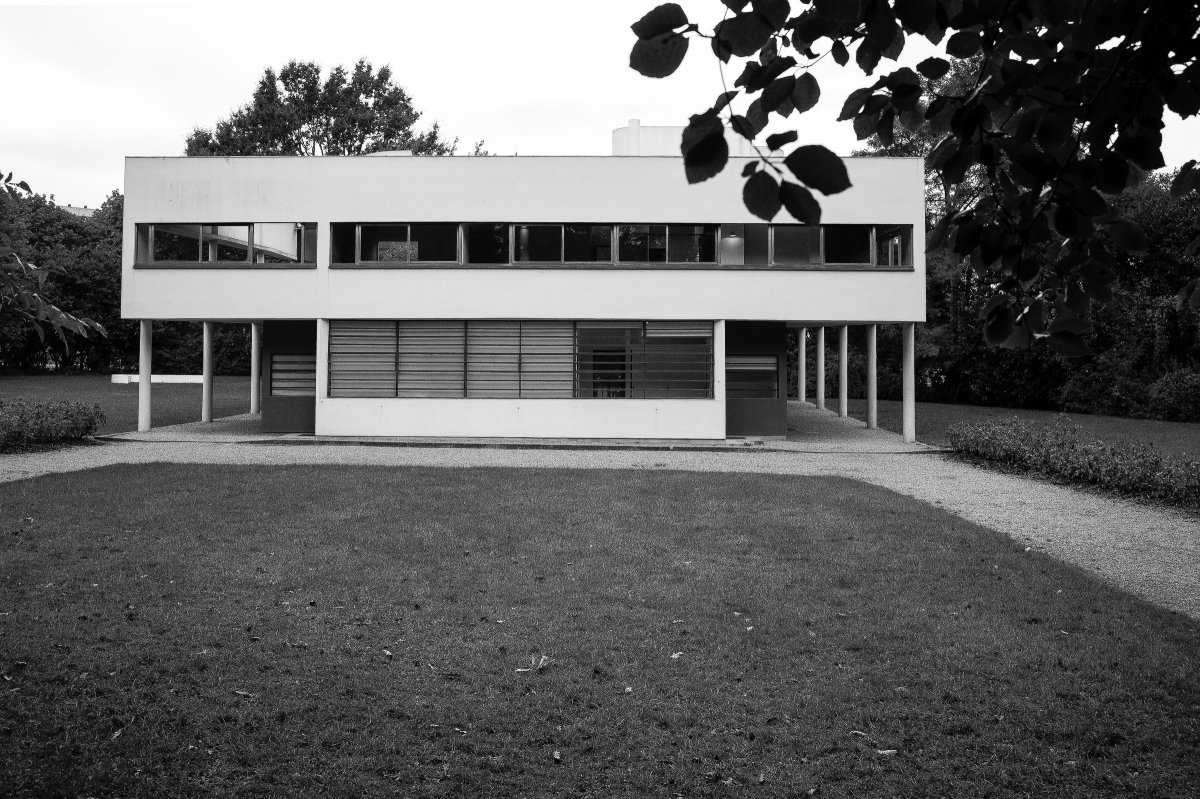
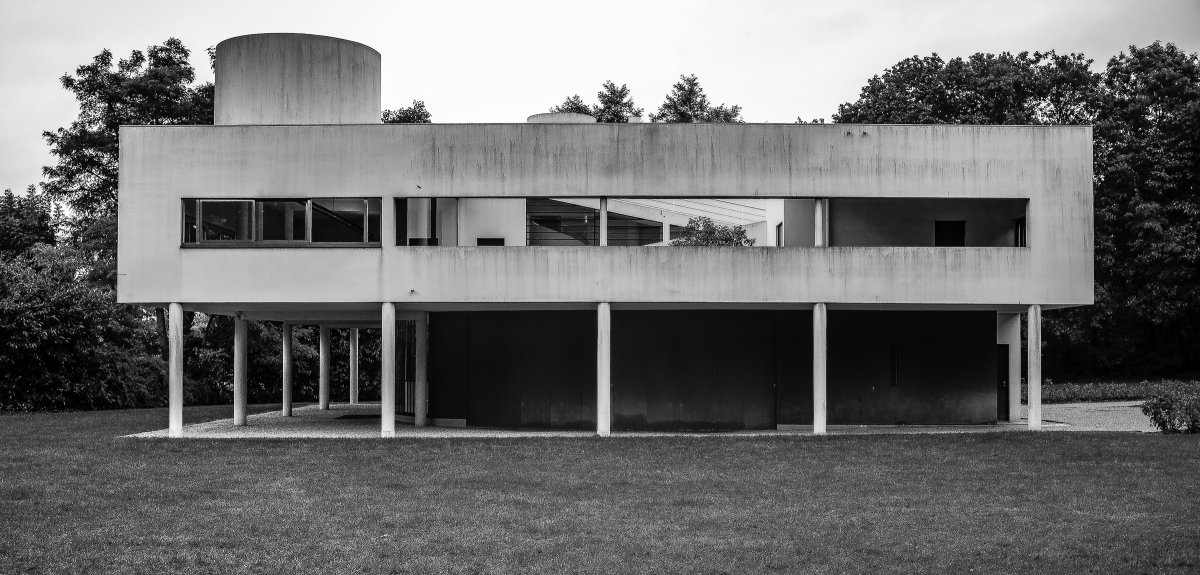
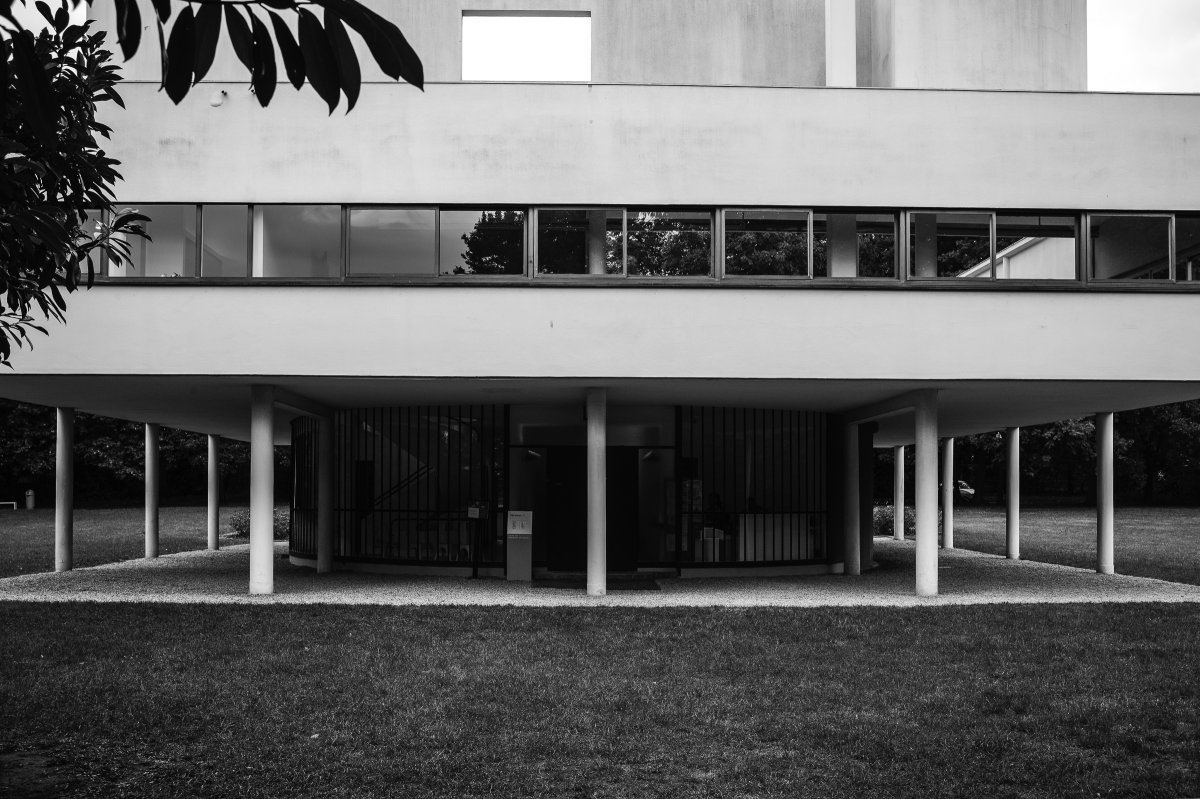
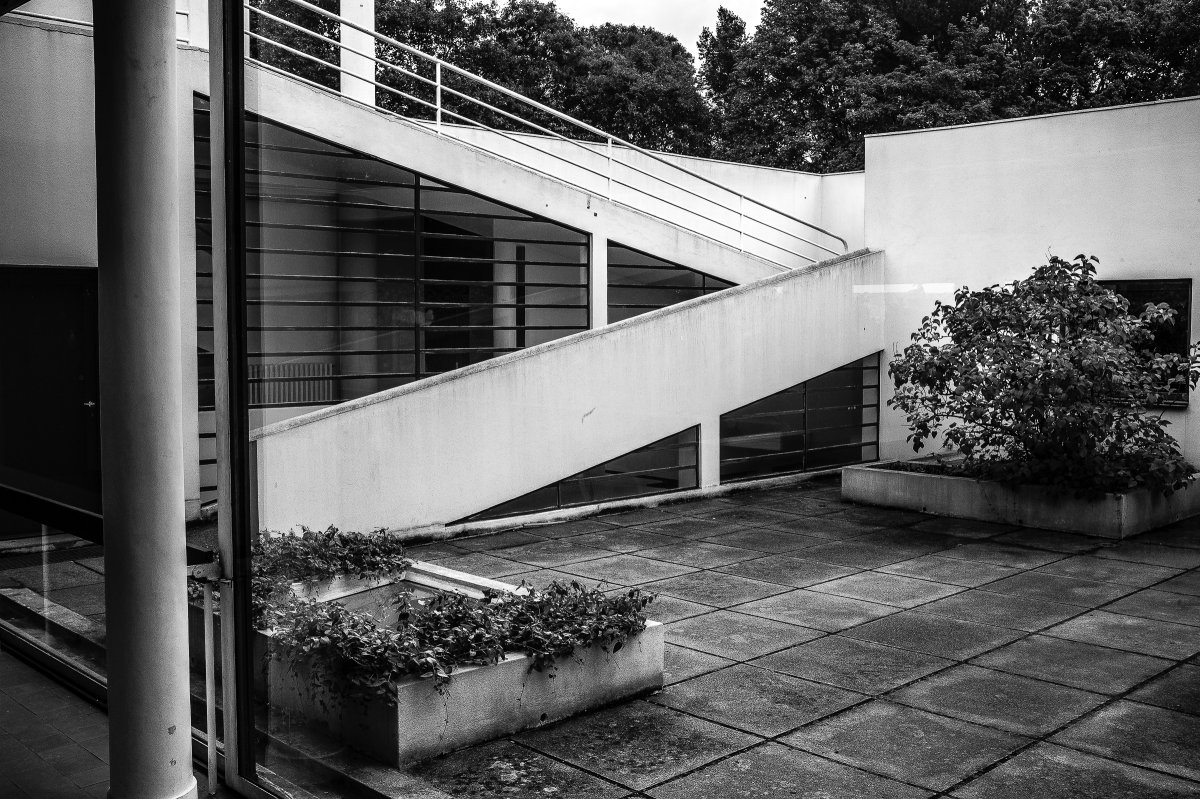
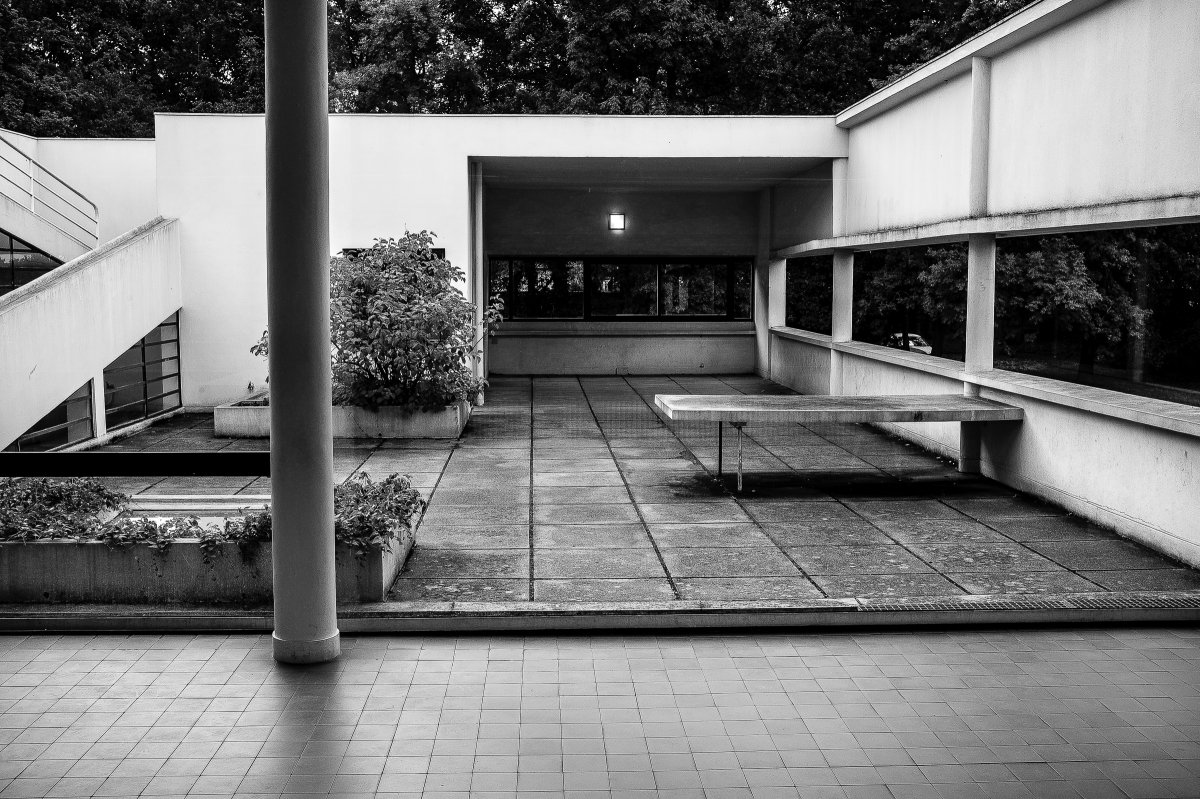
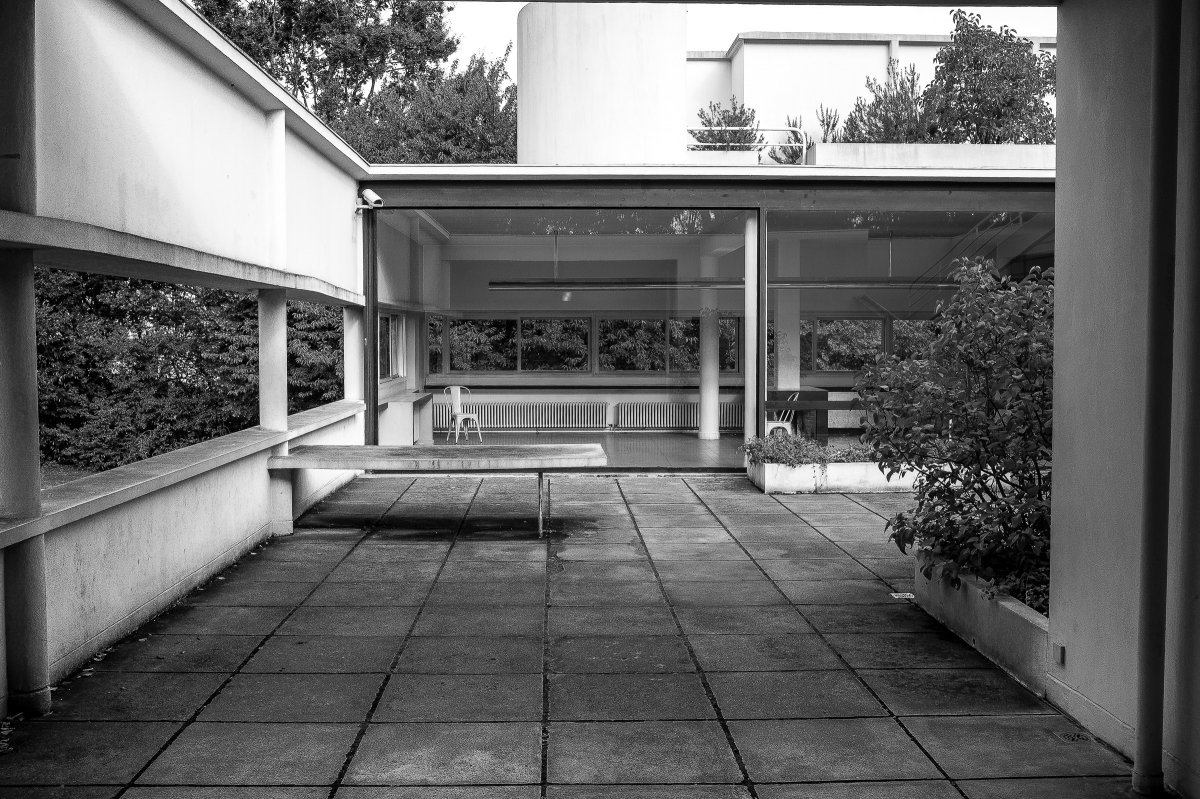
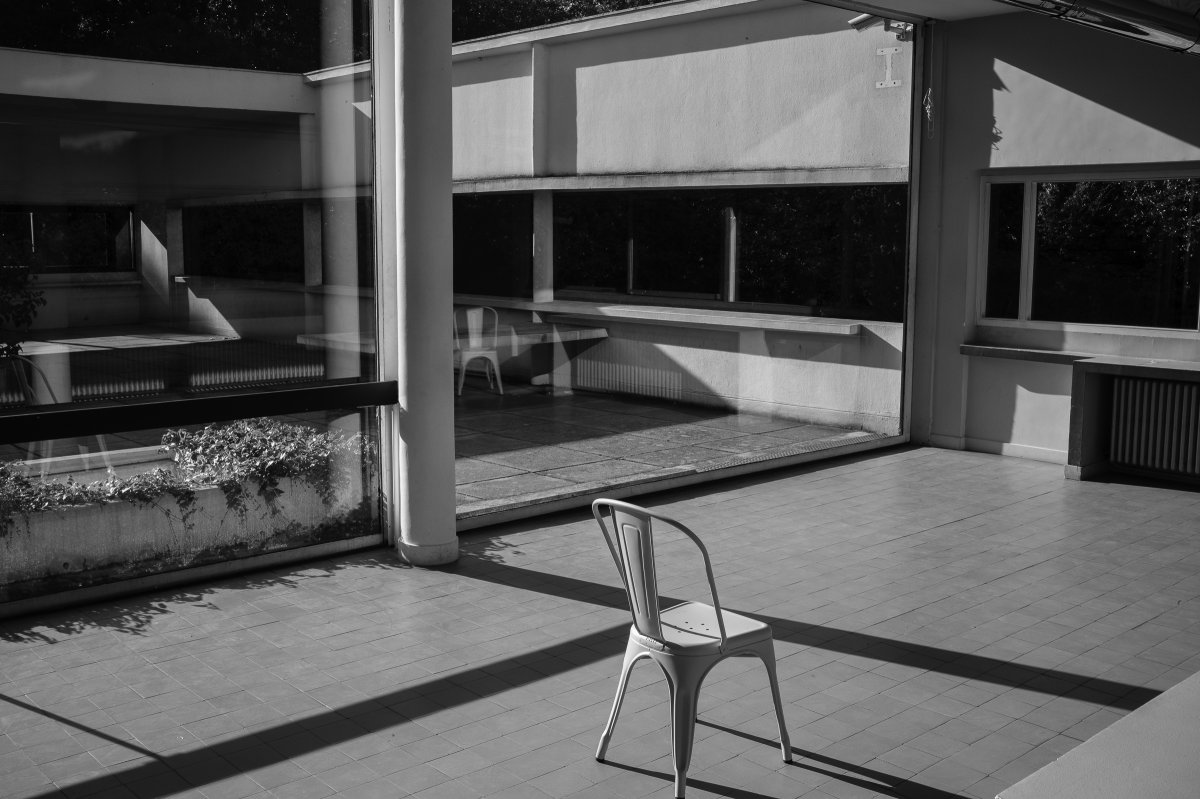
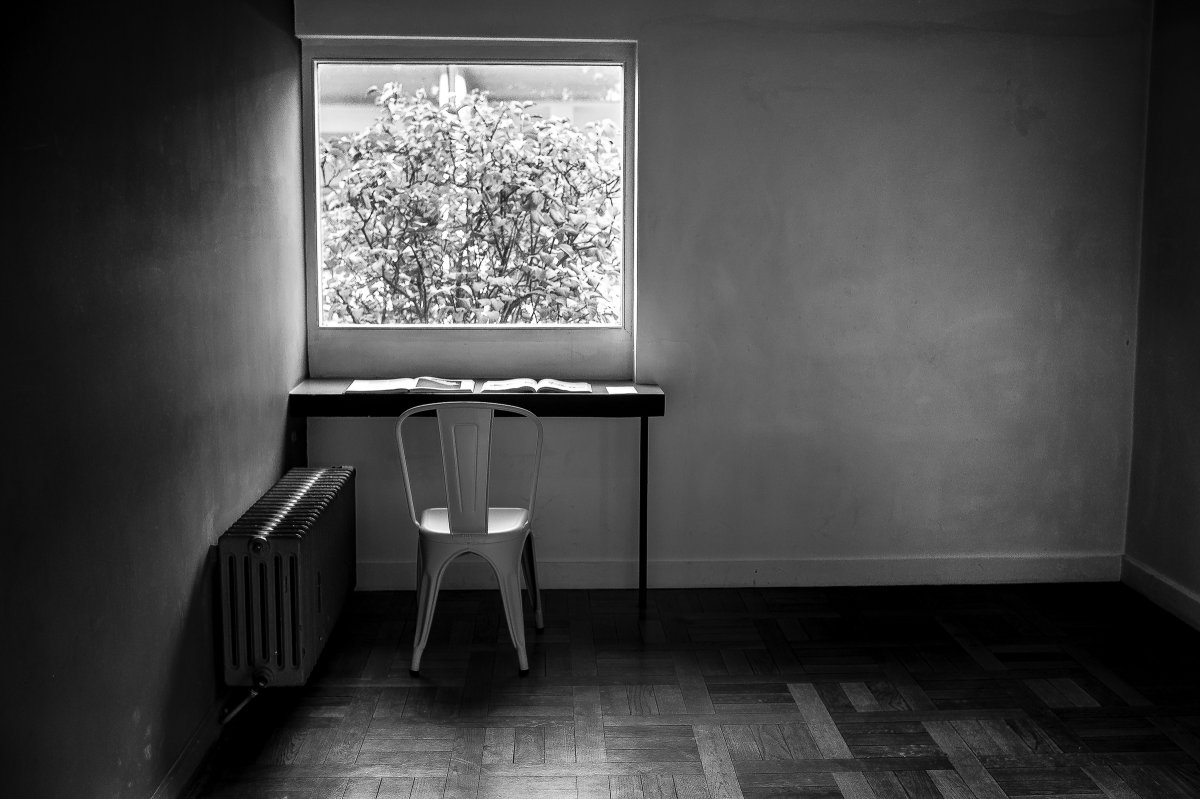
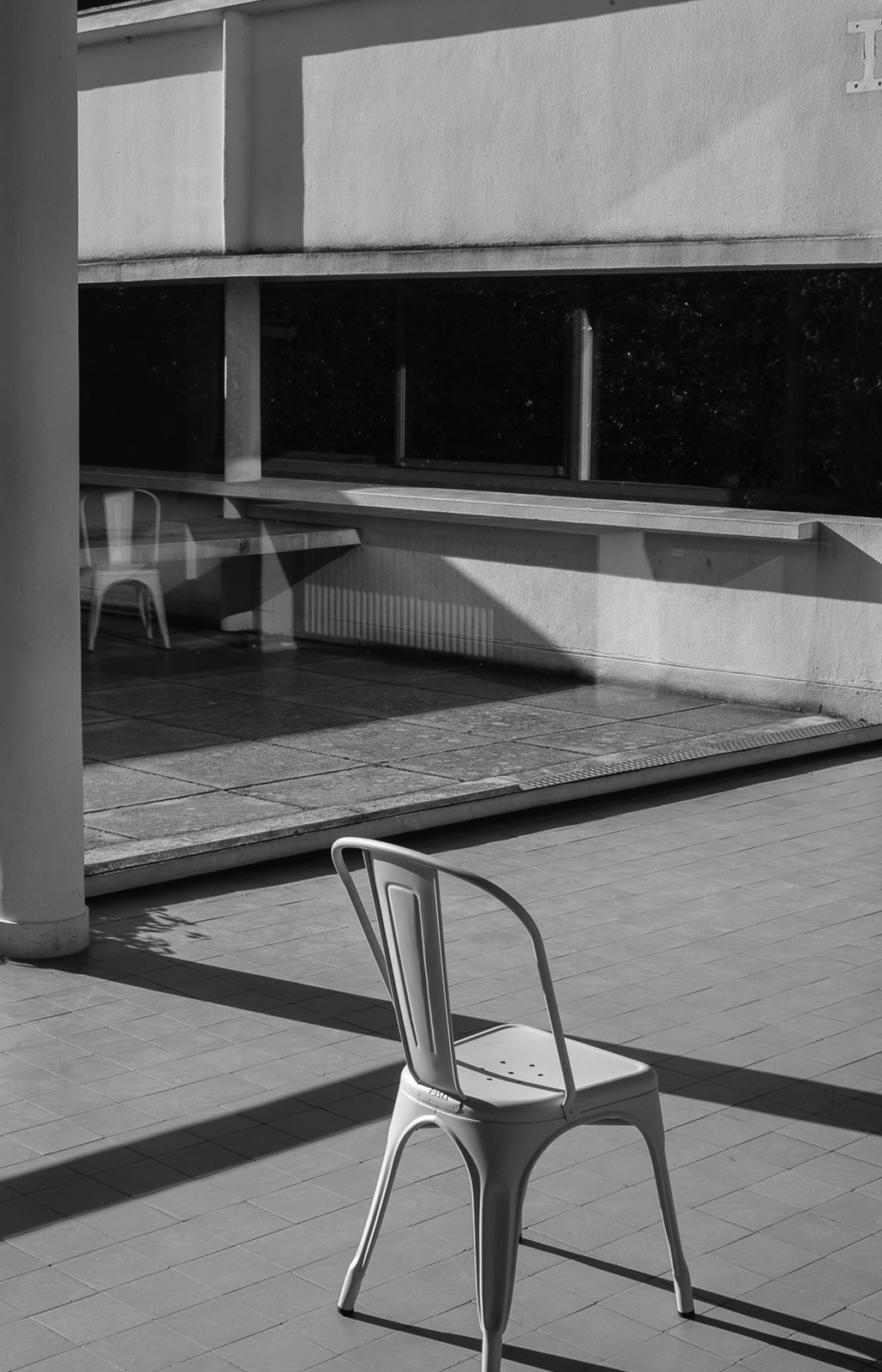
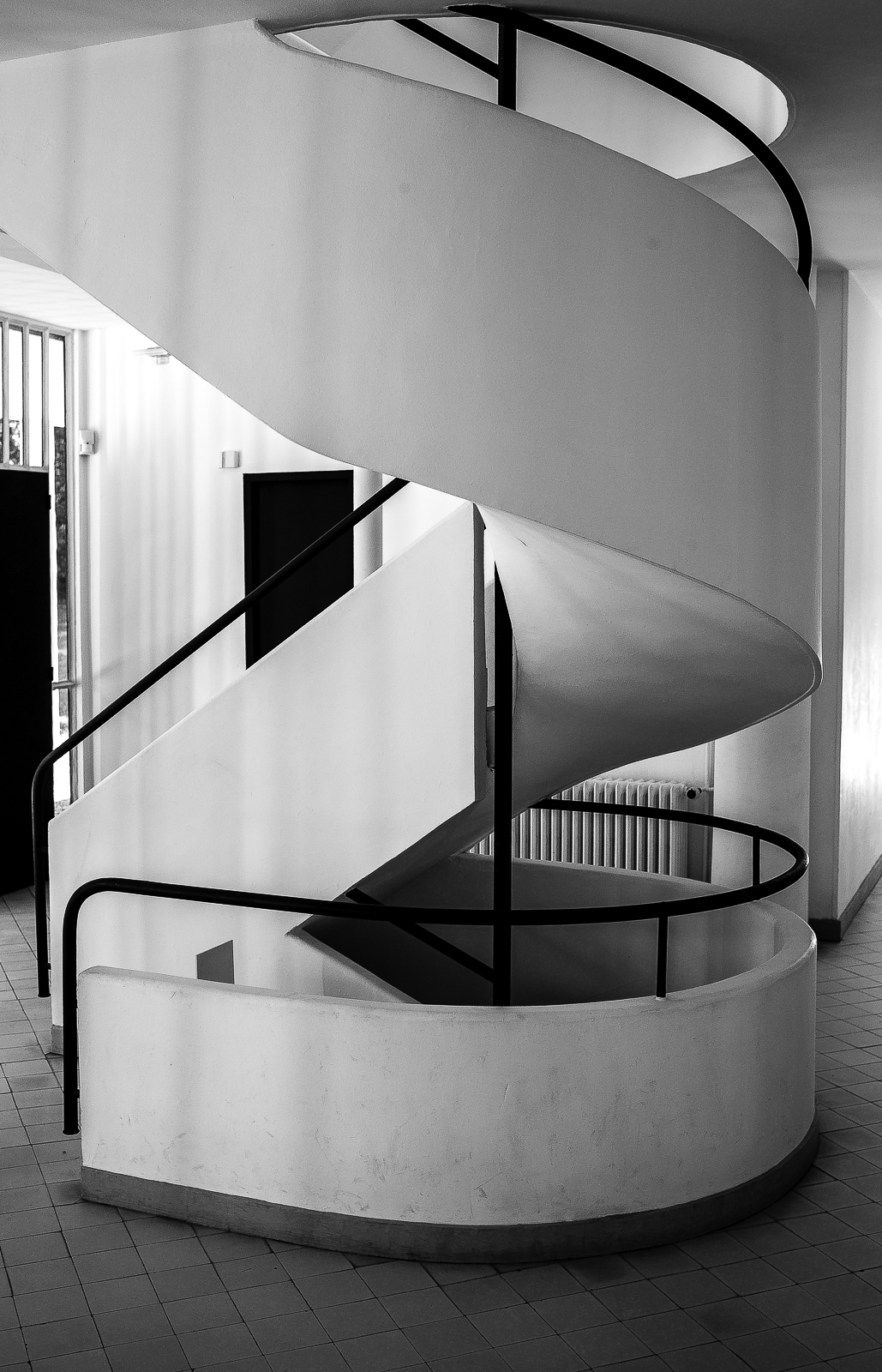
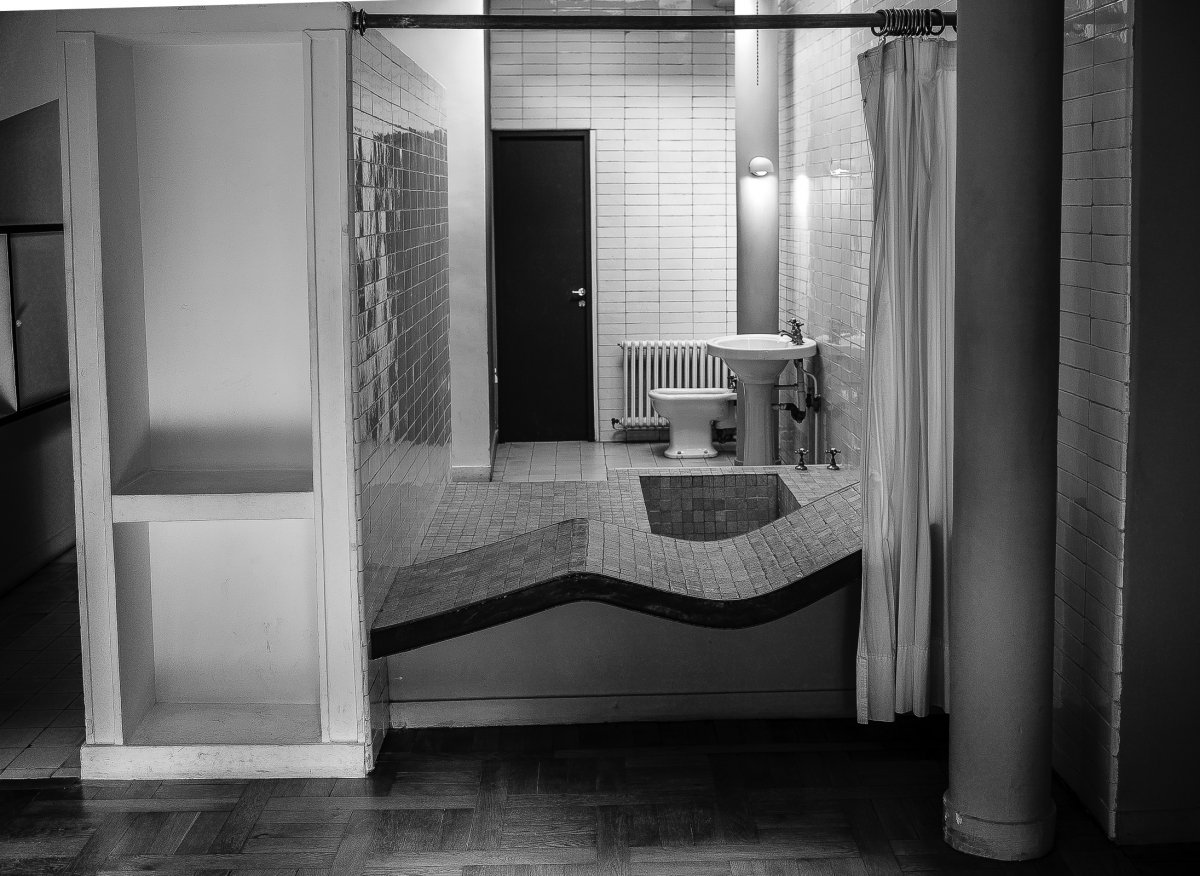
The Villa Savoye, completed in 1931 in Poise, France, by Le Corbusier and Pierre Jeanneret, is one of The most important contributions to modern architecture of The 20th century and an outstanding example of The international style. The villas designed by Le Corbusier in the early 1920s demonstrated what he called the "precision" of architecture, with every feature of the design needing to be validated in design and urban terminology.
The house was originally built as a rural resort for the Savoye family. In the spring of 1928, the wealthy French insurance company Pierre Sayoye and his wife Eugenie contacted Le Corbusier and his cousin Pierre Jeanneret, hoping to commission the design. By the end of the 1920s, Le Corbusier had become an internationally renowned architect and was regarded as a leading figure in modern architecture.
Le Corbusier used reinforced concrete and plaster masonry to build the Villa Savoy. The use of reinforced concrete was a very modern construction method in the 1920s and 1930s. The Villa Savoye is Le Corbusier's five-point vision for a new building, which contains his ideas and concepts of open plan and free space. This means that Corbusier needs to use materials with complete structure.
- Architect: Le Corbusier(1887~1965)
- Words: Qianqian