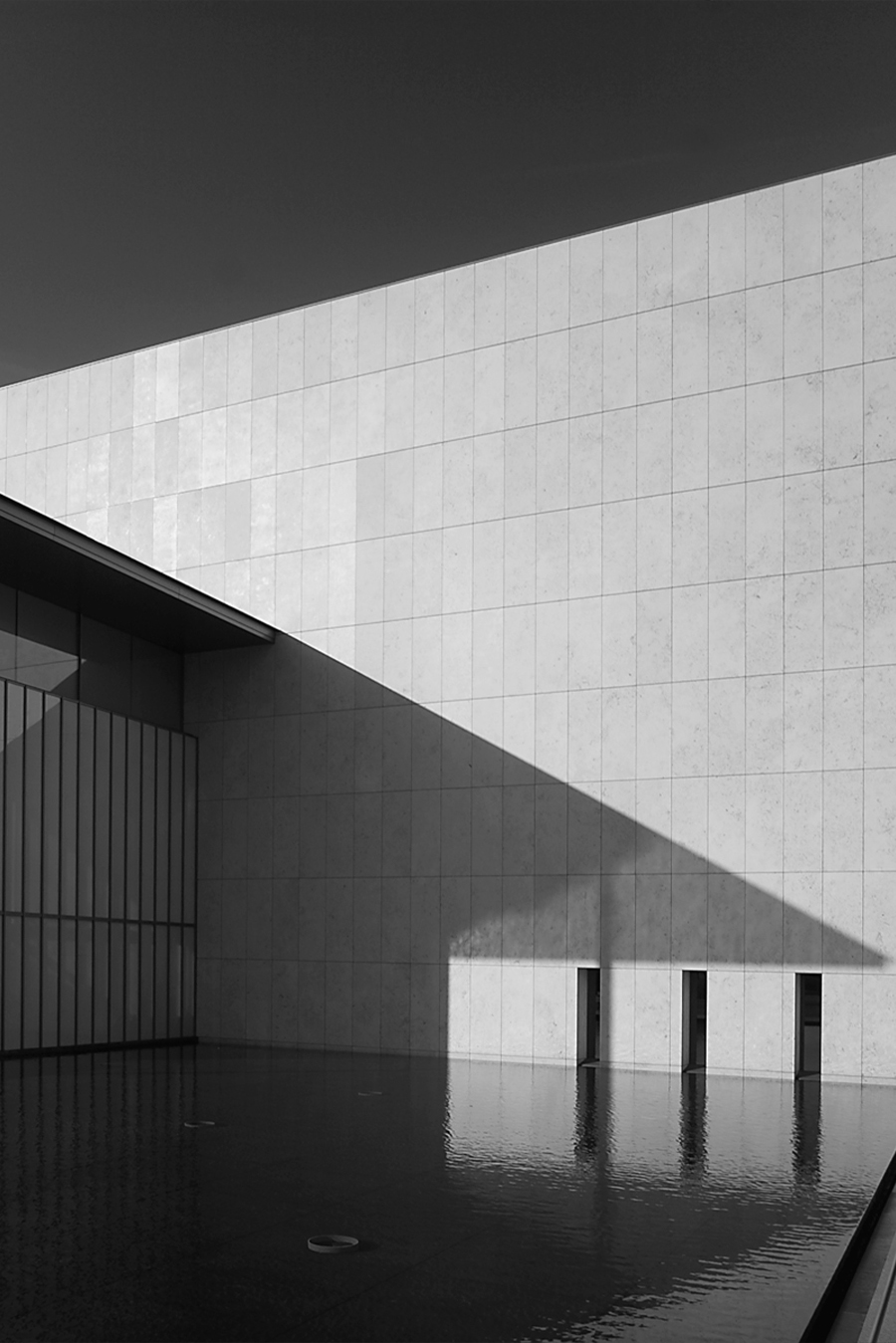
The almost 18.000 m2 new wing now houses some of Japan’s most important artworks, so it was key that the building, including the storage and exhibition facilities, was earthquake secured to the highest technological standards. In fact, the completed building has been left empty for a whole year before the opening just to make sure the construction materials and paints are all set.
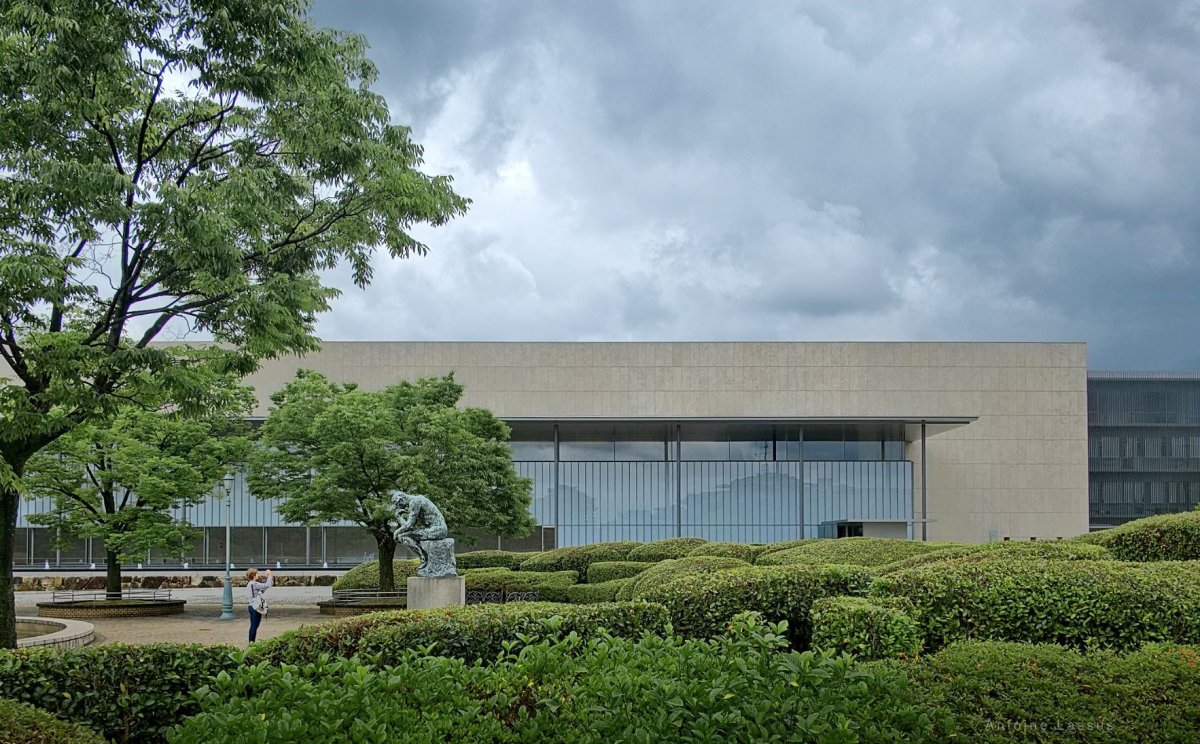
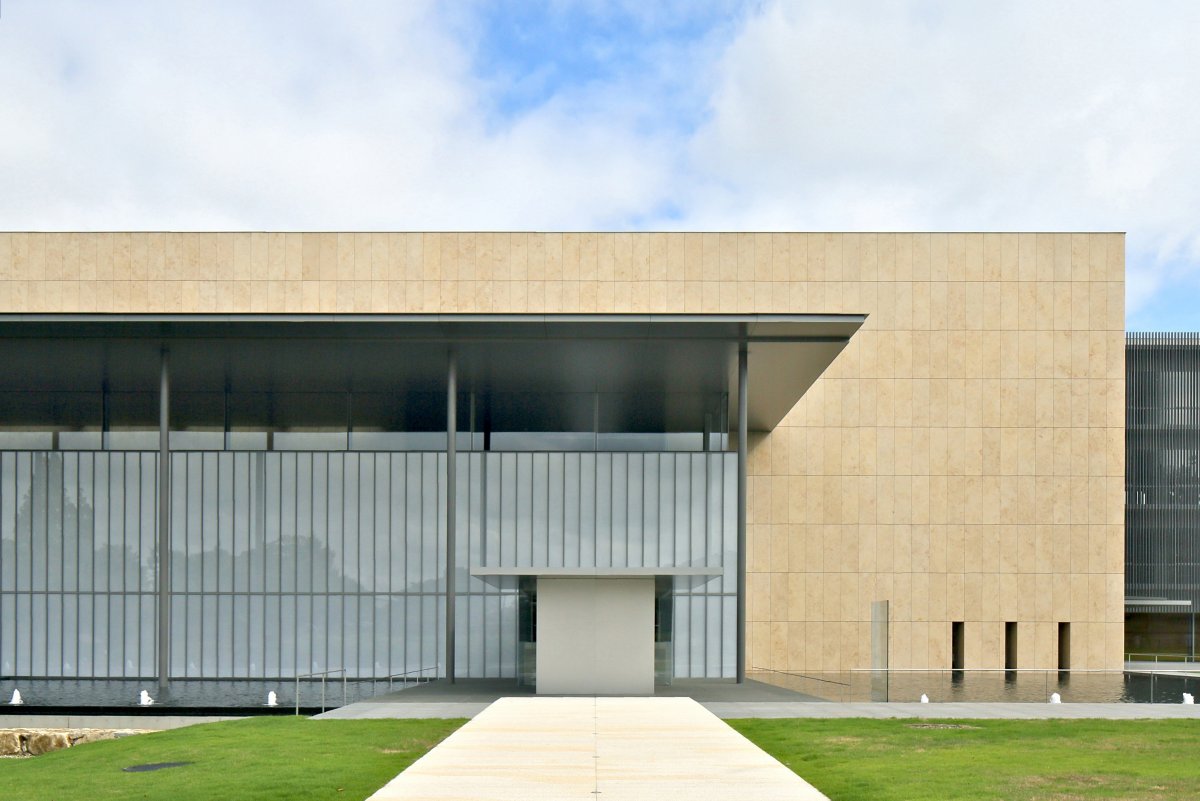
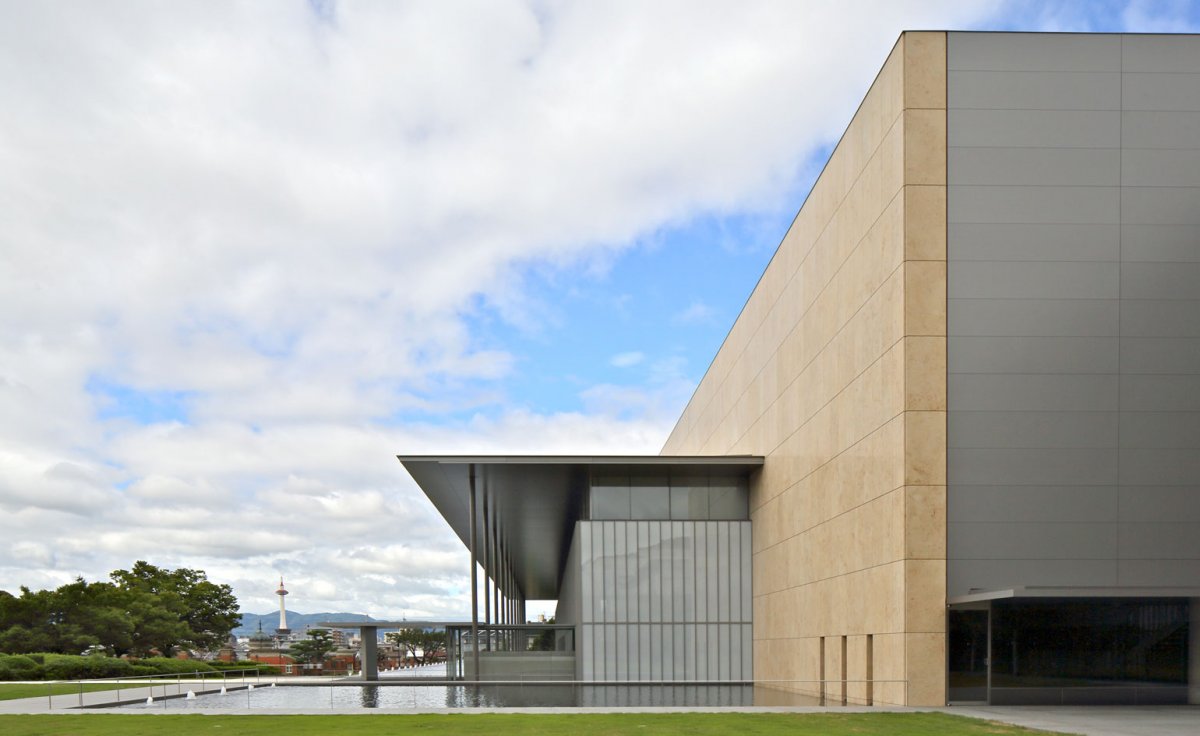
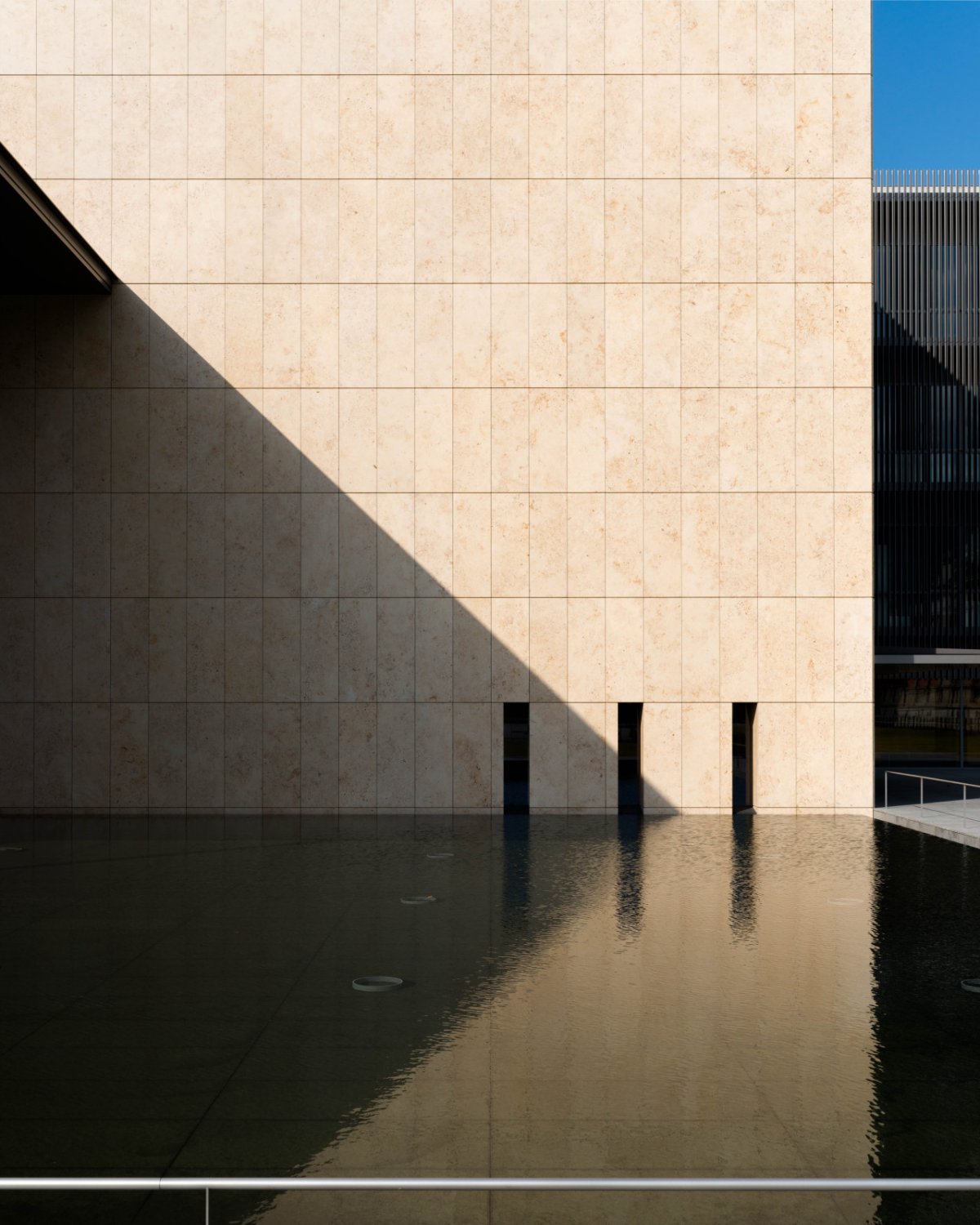
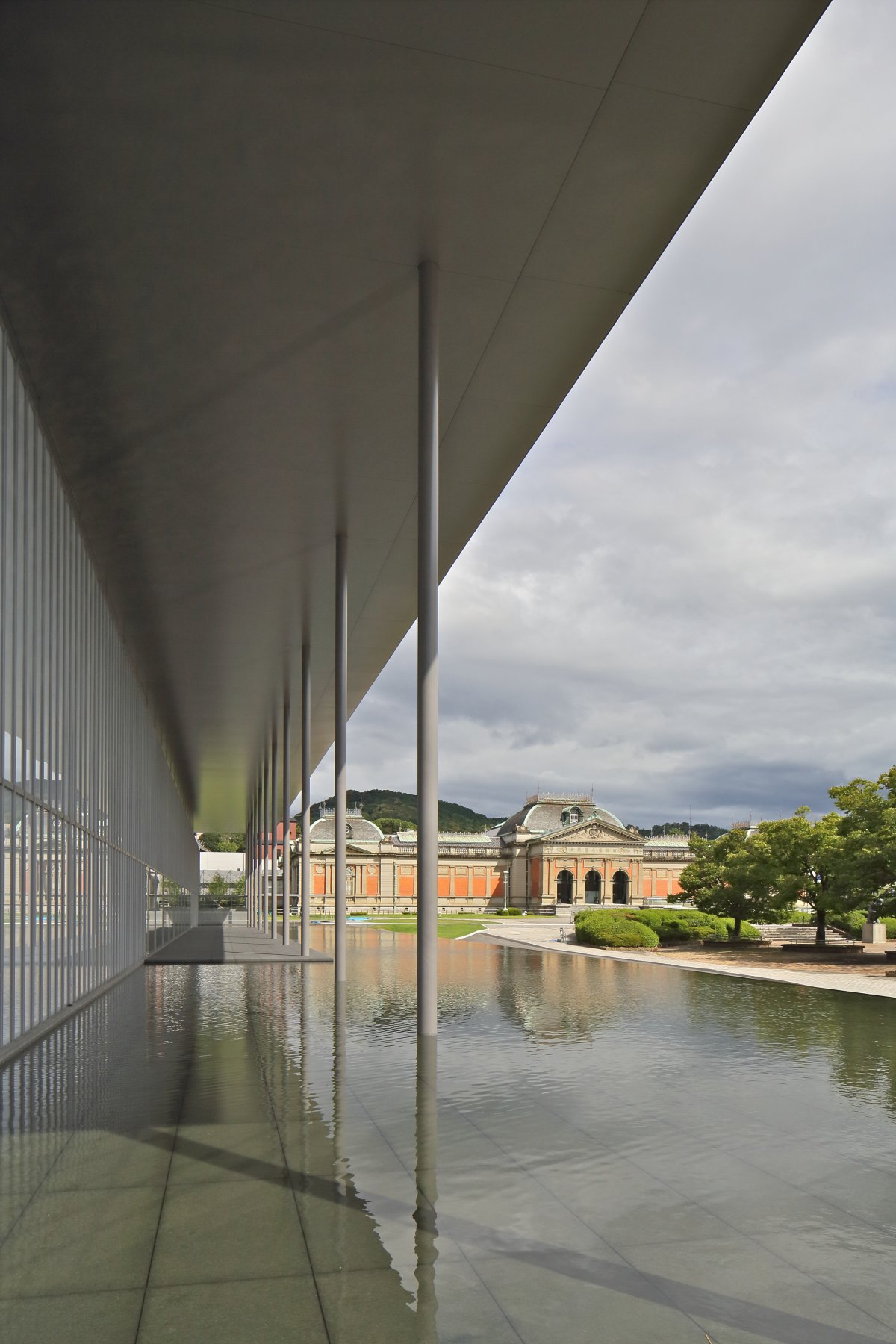
Known as the Meiji Kotokan, Kyoto National Museum’s main building dates back from 1895 and, with its red-brick French Renaissance ornamental style, it could not be more different from Taniguchi’s strict geometrical and modern architecture in glass, steel and limestone. Taniguchi - who is also behind the redesign of the Museum of Modern Art in New York - hasn’t tried to hide this, but has made some considerations to facilitate the juxtaposition between these two very different buildings.
The height of the new building’s portico roof is kept at the same level as the old building’s eaves. Two stories of the new wing have been constructed underground to minimise the volume of the rather large building, so as not to overpower the existing Meiji Kotokan.
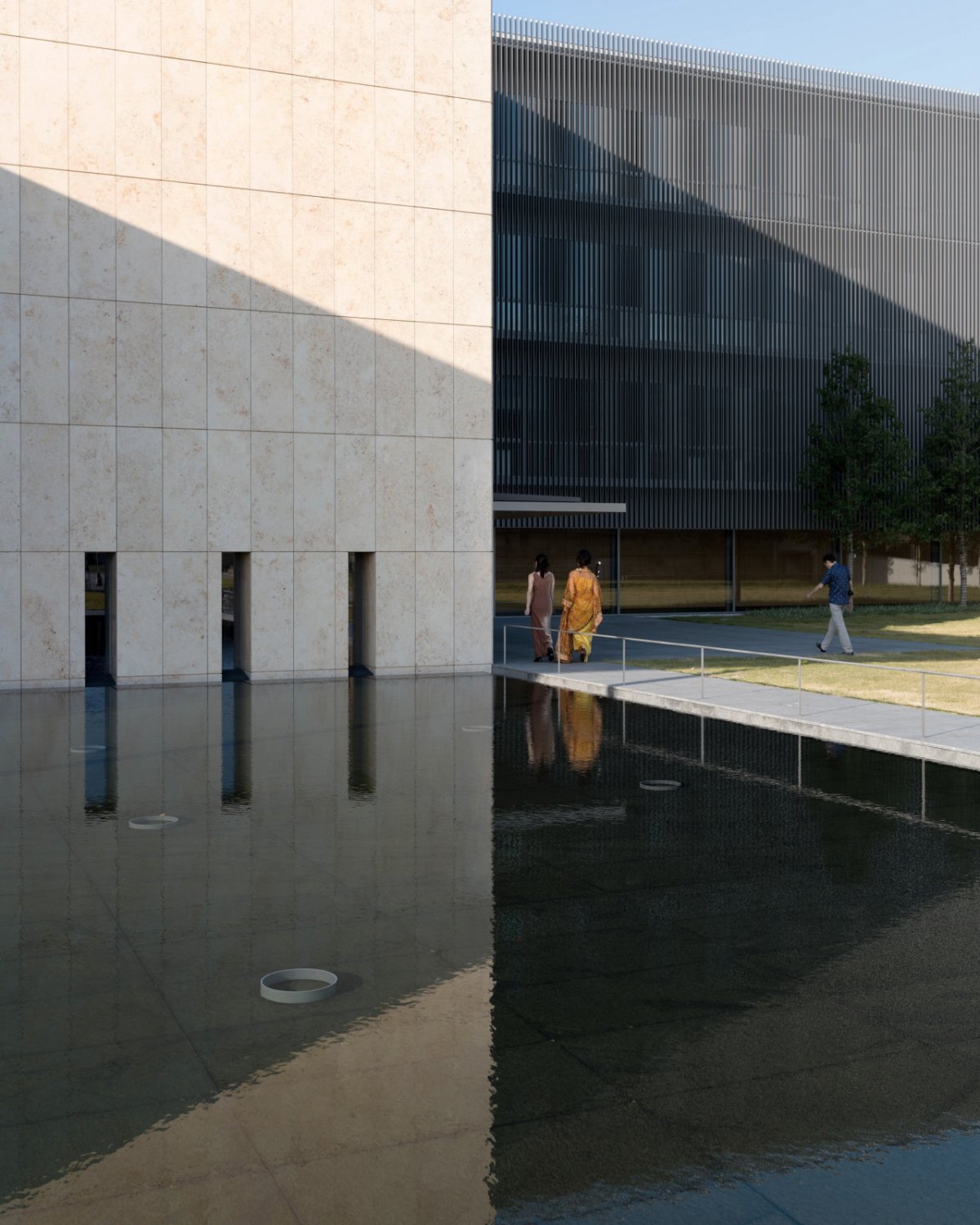
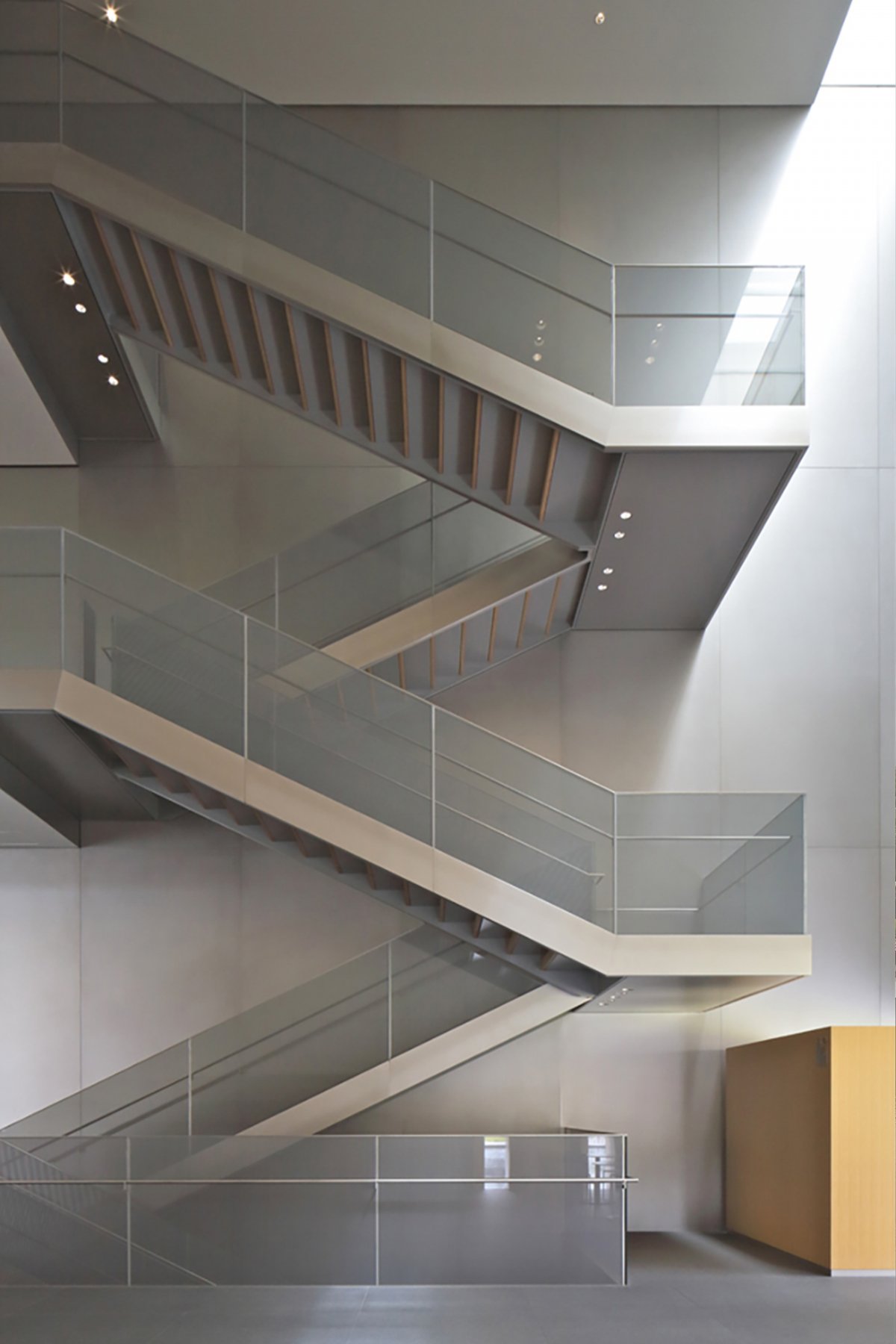
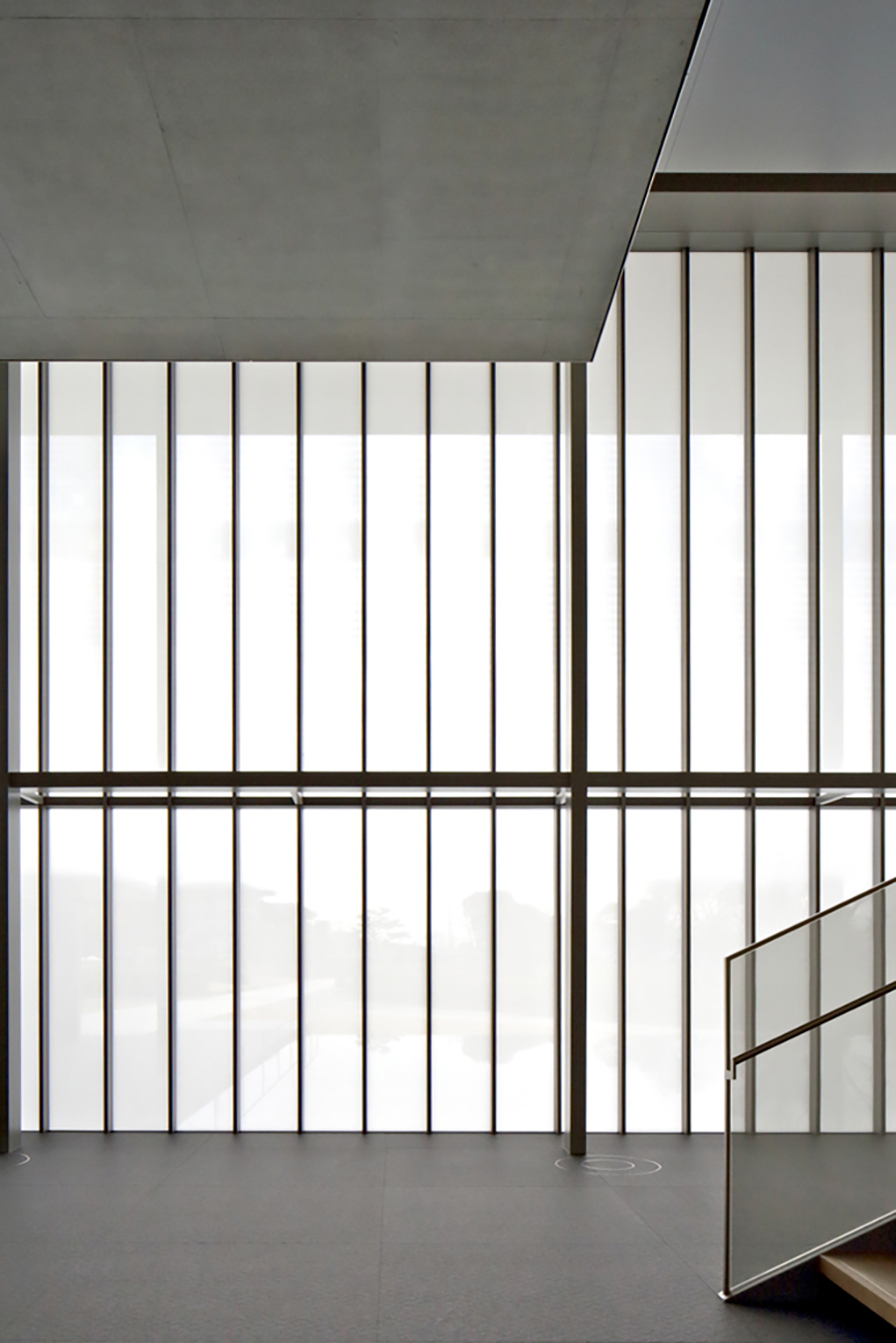
The interiors are sharply divided in two. The exhibition and storage areas are completely shut off from natural light and feature the latest in climate control technology to preserve the precious cultural artefacts in the museum’s archives. The front lobby, restaurant and offices are kept much more open and allow vistas of the surrounding greenery and Kyoto neighbourhoods.
Next up is landscaping. Taniguchi is planning to revamp the large central garden on the complex to better connect these two very distinct buildings.
- Architect: Yoshio Taniguchi
- Photos: Kitajima Toshiharu
- Words: Gina